T4 Back Pain: Understanding, Managing, and Preventing It
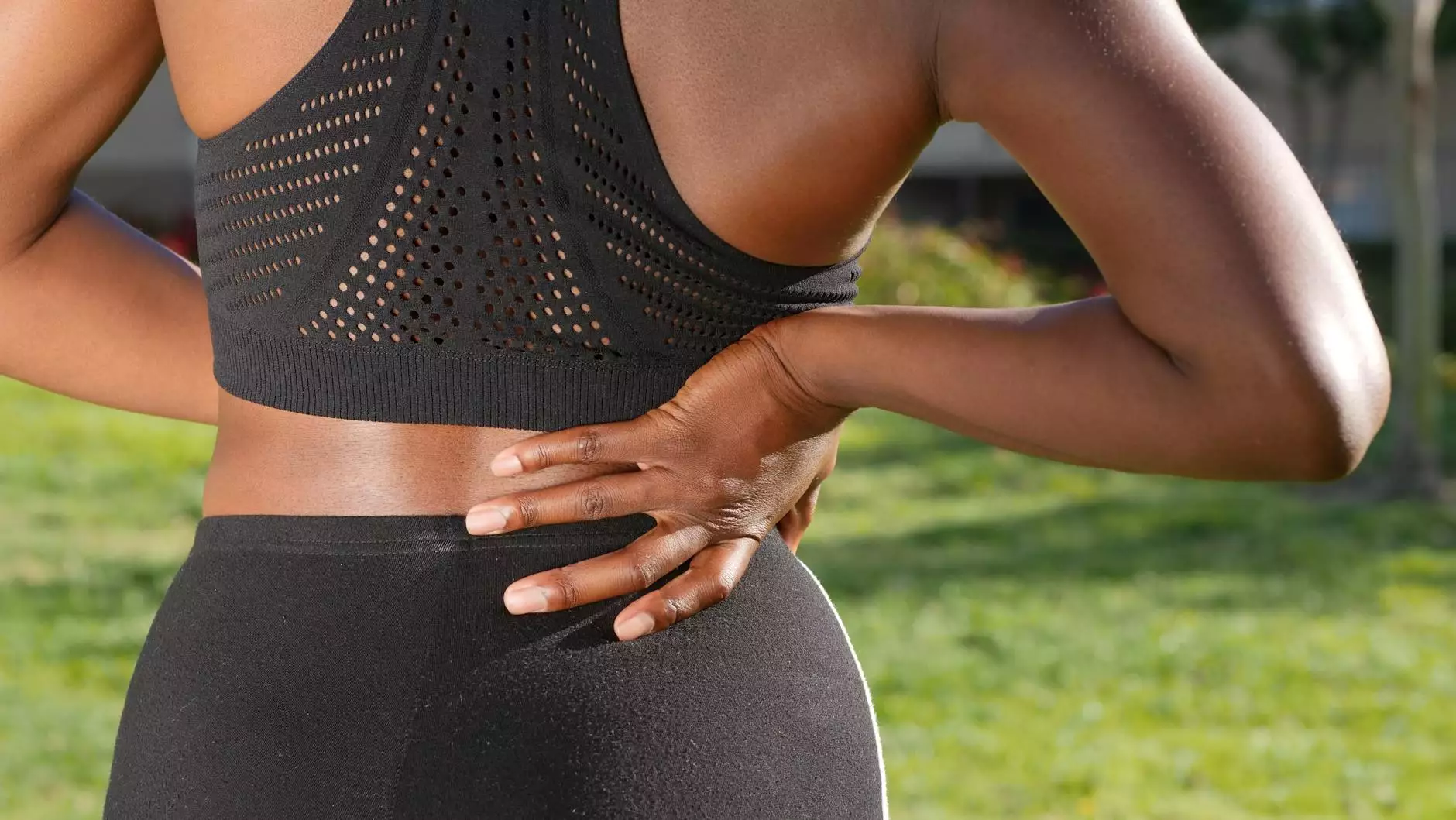

T4 back pain is a term that refers to discomfort or pain associated with the fourth thoracic vertebra in the spine. This area of the back is crucial as it provides stability and support to the upper body while facilitating essential movements. Understanding the nuances of T4 back pain can assist individuals in seeking proper treatment and effectively managing their symptoms.
What is T4 Back Pain?
T4 back pain specifically pertains to discomfort that arises in the thoracic region of the spine, particularly near the fourth vertebra. The thoracic spine consists of 12 vertebrae, and each vertebra connects with rib bones, forming the ribcage that protects vital organs. Pain in this area can stem from various sources, including muscle strain, poor posture, injuries, or underlying medical conditions.
Causes of T4 Back Pain
Various factors can contribute to the development of T4 back pain. Understanding these causes is pivotal in effective management:
- Muscle Strain: Overexertion or improper lifting techniques can strain the muscles surrounding the T4 vertebra.
- Poor Posture: Spending prolonged periods in a hunched position can lead to strain on the thoracic spine.
- Injuries: Accidents, falls, or sports injuries can impact the T4 vertebra, resulting in pain.
- Osteoarthritis: Degenerative changes within the joints can lead to discomfort in the thoracic spine.
- Herniated Discs: Discs can rupture and compress nearby nerves, causing pain. Although this is more common in the lumbar spine, it can occur in the thoracic region.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions such as scoliosis or osteoporosis can lead to structural changes, resulting in pain.
Symptoms of T4 Back Pain
Identifying the symptoms associated with T4 back pain is essential for diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Localized Pain: Pain is often felt directly over the T4 vertebra and may radiate.
- Muscle Tightness: Accompanying tightness may be present in the surrounding muscles.
- Stiffness: Individuals may experience reduced range of motion in the upper back.
- Referred Pain: Pain may radiate to the shoulder, neck, or even the abdomen in some cases.
- Numbness or Tingling: If nerves are affected, there may be sensations of numbness or tingling.
Diagnosis of T4 Back Pain
Proper diagnosis is key to addressing T4 back pain effectively. Healthcare providers often follow a systematic approach, including:
- Patient History: Understanding the patient’s medical history, lifestyle, and the nature of the pain.
- Physical Examination: Conducting a physical exam to check for tenderness, range of motion, and muscle strength.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI, or CT scans may be employed to visualize the spine and identify structural issues.
- Other Diagnostic Tests: Blood tests might be conducted to rule out infections or inflammatory conditions.
Treatment Options for T4 Back Pain
Managing T4 back pain entails a multi-faceted approach tailored to the individual's needs. Some of the treatment options include:
1. Conservative Treatments
These often involve non-invasive strategies:
- Rest: Allowing adequate time for recovery is crucial, especially after an injury.
- Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises can strengthen the muscles supporting the spine and improve flexibility.
- Chiropractic Care: Chiropractors use spinal manipulation techniques to restore alignment and relieve pain.
- Massage Therapy: Therapeutic massage can reduce muscle tension and improve circulation to the affected area.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Alternating heat and ice packs can mitigate pain and swelling.
2. Medication
Over-the-counter and prescription medications can offer relief:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
- Muscle Relaxants: Useful for managing muscle spasms.
- Pain Relievers: Acetaminophen and other pain relief medications may be recommended.
3. Surgical Options
In rare cases where conservative measures fail, surgical intervention may be necessary:
- Decompression Surgery: Relieves pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
- Spinal Fusion: Stabilizes the spine if vertebrae are damaged or misaligned.
Prevention of T4 Back Pain
Preventative measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing T4 back pain. Here are some strategies:
- Maintain Good Posture: Be mindful of your posture while sitting, standing, and lifting.
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity strengthens the back and core muscles.
- Ergonomic Workstations: Set up a workspace that promotes proper posture and reduces strain.
- Incorporate Stretching: Stretching can enhance flexibility and reduce muscle tightness.
- Use Proper Lifting Techniques: Avoid awkward movements and carry objects close to your body.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Individuals experiencing severe, persistent, or worsening T4 back pain should seek professional medical advice promptly. Key warning signs include:
- Severe Pain: Pain that is disproportionate to the injury.
- Numbness or Weakness: Inability to feel or move parts of the body.
- Bowel or Bladder Dysfunction: Loss of control can indicate serious issues.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Sudden weight loss can signify underlying health problems.
- Fever or Chills: Signs of infection may need immediate attention.
Conclusion
T4 back pain is a common yet manageable condition that can be addressed through a variety of treatment and prevention strategies. Early diagnosis and intervention play a crucial role in successful recovery and quality of life. Whether through conservative methods such as physical therapy and medication or more aggressive surgical approaches, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for a tailored treatment plan. Stay informed, remain proactive about your spinal health, and seek help when needed to navigate the challenges associated with T4 back pain.
For more information on managing back pain and other related health issues, visit iaom-us.com, where you’ll find a wealth of resources and expert advice.